
Cell phones have become an integral part of our lives, and it is hard to imagine a day without them. However, with the increasing use of wireless microphone systems in various settings, it has become a concern whether cell phones interfere with wireless microphones.
Understanding wireless microphone systems is essential to identify the potential for interference. Wireless microphones are susceptible to interference from various sources, including cell phones. Interference can cause unwanted noise, dropouts, or complete loss of signal, leading to an unpleasant experience for the audience.
In this article, I will explore the different types of interference in wireless microphones and how to mitigate them.
Key Takeaways
- Cell phones can interfere with wireless microphones, causing unwanted noise or signal loss.
- Frequency coordination is crucial in minimizing interference in wireless systems.
- Practical solutions such as turning off cell phones or using frequency coordination tools can help minimize interference.
Table of Contents
Can Cell Phones Interfere With Wireless Microphones?
Cell phones can interfere with wireless microphones. Both cell phones and wireless microphones operate using radio frequency (RF) signals, and when they are in close proximity to each other, there is a potential for interference.
Wireless microphones typically use specific frequency bands allocated for audio transmission. Cell phones, on the other hand, operate on various frequency bands depending on the network technology (e.g., 2G, 3G, 4G, 5G).
Sometimes, these frequency bands can overlap with the ones used by wireless microphones, especially in unlicensed frequency ranges, causing interference.
The interference can manifest in different ways, such as dropouts, audio distortion, or even complete loss of audio transmission in the affected wireless microphone system.
The severity of the interference depends on factors like the proximity of the cell phone to the wireless microphone receiver, the strength of the cell phone signal, and the quality of the wireless microphone system’s design and shielding.
To minimize interference, wireless microphone users should carefully choose their frequency bands and avoid frequencies that are commonly used by nearby cell towers or other wireless devices.
Additionally, high-quality wireless microphone systems often incorporate features like frequency agility and spectrum scanning to find and use the least congested frequencies in the area.
In some professional settings, specific frequency bands have been reserved exclusively for wireless microphone use to reduce the likelihood of interference with other wireless devices like cell phones.
Understanding Wireless Microphone Systems
Wireless microphone systems are a popular choice for performers, public speakers, and event organizers who require mobility and flexibility. In a typical sound system, one wireless system replaces one standard wired microphone. The wireless system eliminates the need for a cable that connects the microphone to the sound system, giving the user greater freedom to move around.
Wireless microphone systems are like small radio stations. They have a transmitter that sends the audio signal to a receiver, which then sends the signal to the sound system. The transmitter can be located inside the microphone or in a separate bodypack. The receiver is usually stationary and connected to the sound system.
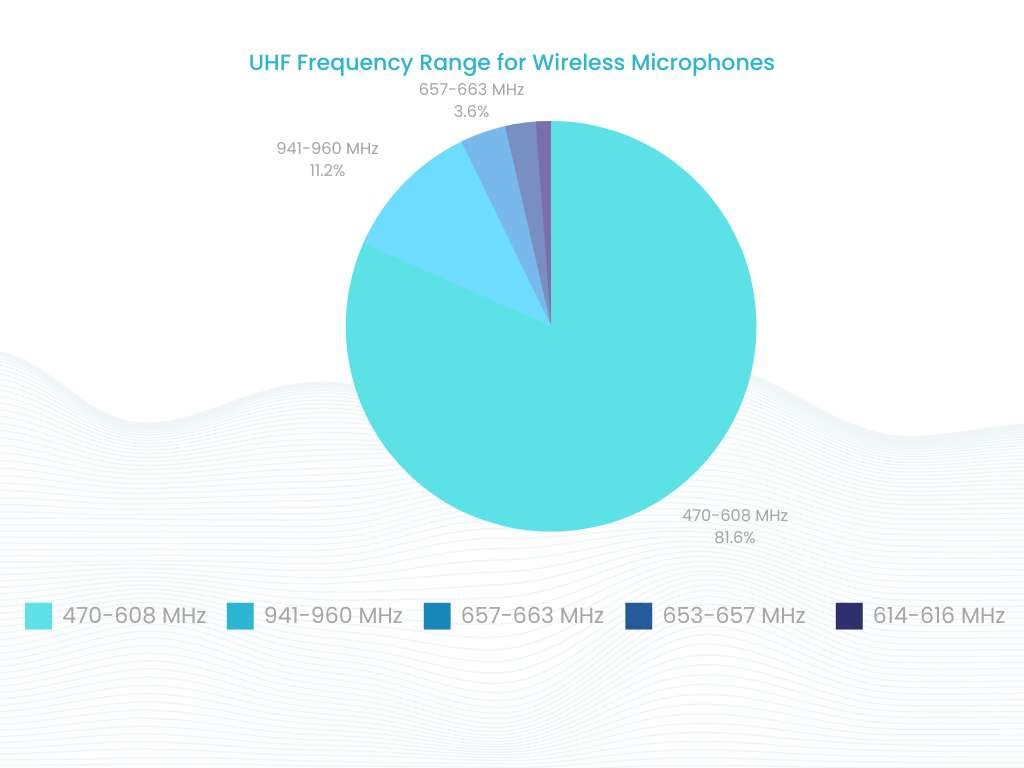
Wireless microphone systems operate within a specific frequency range. The frequency range determines the available channels that the system can use. The frequency range can vary depending on the system, but most systems operate within the UHF (Ultra High Frequency) range, which is between 470 MHz and 698 MHz.
It is important to note that wireless microphone systems share the same frequency range as other wireless devices, such as cell phones and Wi-Fi networks. This means that interference can occur if the wireless microphone system and another device are operating on the same frequency. Interference can cause dropouts, static, and other audio issues.
To avoid interference, it is essential to choose a wireless microphone system with a frequency range that is not in use by other wireless devices in the area. It is also important to scan the frequency range before using the system to ensure that there are no other devices operating on the same frequency.
Interference in Wireless Microphones
Wireless microphones are prone to interference from various sources, including cell phones. Interference can cause unwanted sounds, such as static, hissing, and crackling, which can be distracting and disruptive to the audio quality.
There are two types of interference that can affect wireless microphones: direct interference and squelch interference. Direct interference occurs when a signal from another device is received by the microphone’s receiver, causing unwanted sound. Squelch interference, on the other hand, occurs when the microphone’s receiver is unable to distinguish between the desired signal and unwanted noise.
Non-wireless interference can also affect wireless microphones. This type of interference is caused by electrical devices, such as power lines, fluorescent lights, and motors. Non-wireless interference can cause unwanted sound and reduce the microphone’s range.
The noise floor is another factor that can affect wireless microphones. The noise floor is the level of unwanted sound that is present in the environment. A high noise floor can make it difficult for the microphone to pick up the desired signal, resulting in poor audio quality.
Intermodulation distortion is another issue that can affect wireless microphones. Intermodulation distortion occurs when two or more signals combine to create unwanted harmonics that interfere with the desired signal. This can result in distorted audio and reduced range.
To minimize interference in wireless microphones, it is important to use high-quality equipment and to select a frequency that is not being used by other devices. It is also important to properly position the microphone and to use a high-quality antenna.
Cell Phones and Wireless Microphone Interference
Wireless microphones and cell phones operate on different frequency ranges. However, the proximity of the frequencies used by both devices can cause interference in some situations. Here’s what you need to know about cell phones and wireless microphone interference:
- GSM and iDEN (voice connect service from Nextel) were originally based on Time Division Multiple Access (TDMA), which has been around for a long time and is being replaced by newer technology. GSM buzz and noise can cause interference with wireless microphones.
- Individual cellular devices generally do not interfere with wireless microphone systems. But, smartphones and other wireless signal devices, including cell phones that are WiFi capable, can and do interfere with wireless microphones. This is especially true for mics using the 2.4 GHz band, which are less common than industry standard UHF mics.
- For all practical purposes, cellular transmissions do not directly interfere with wireless audio devices. However, the 700, 800, and 850 MHz bands used by cell phone networks can cause interference when they are in close proximity to wireless microphones that operate on the 470 – 698 UHF-TV band.
- If you experience interference, there are a few things you can do to avoid it. Switch off your phone, move away from the wireless microphone, or try using a different frequency.
Frequency Coordination in Wireless Systems
Frequency coordination is one of the most critical aspects to consider when setting up a wireless microphone system. It involves selecting the appropriate frequencies for the wireless system to operate on to ensure that it does not interfere with other wireless systems operating in the same area.
When selecting frequencies for a wireless system, it is important to consider the frequency bands available for use.
Shure USA identifies each range as a frequency band with a letter and number, like G50 or J53. These frequency bands are regulated by the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) and are subject to change.
To ensure that the wireless system operates smoothly, it is important to coordinate the frequencies used with other wireless systems operating in the same area. This is especially important in urban areas where multiple wireless systems may be operating in close proximity.
When coordinating frequencies, it is important to consider the following factors:
- The number of wireless systems operating in the area
- The frequencies used by other wireless systems
- The frequency bands available for use
- The frequency coordination software used
By coordinating frequencies effectively, it is possible to minimize interference and ensure that the wireless microphone system operates smoothly. This can help to prevent dropouts, signal loss, and other issues that can affect the quality of the sound.
Practical Solutions to Minimize Interference
To minimize interference between cell phones and wireless microphone systems, there are several practical solutions to consider. These solutions include:
- Keep Cell Phones Away from Wireless Microphone Systems: The closer a cell phone is to a wireless microphone system, the more likely it is to cause interference. To minimize interference, keep cell phones at least a few feet away from the wireless microphone system.
- Use a High-Quality Receiver: A high-quality receiver can help minimize interference caused by cell phones. Look for a receiver with strong filtering capabilities and a high signal-to-noise ratio.
- Monitor Interference Levels: Using a monitor can help you identify when interference is occurring. If you notice interference, you can adjust the placement of the wireless microphone system or move the cell phone further away.
- Use High-Quality Cables: High-quality cables can help minimize interference caused by cell phones. Look for cables with good shielding and low capacitance.
- Turn Off Cell Phones: Turning off cell phones when they are not in use can help minimize interference. This is especially important when using wireless microphone systems in crowded areas where many cell phones are in use.
Final Thoughts
Cell phones can interfere with wireless microphones, causing annoying noises and disruptions. However, there are ways to avoid this interference, such as switching off your phone or keeping it at a safe distance from the microphone.
As a DJ or performer, it is important to be aware of potential interference issues and take steps to prevent them. This includes selecting the right type of wireless microphone and ensuring that it is properly installed and maintained.
In the United States, the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) regulates the use of wireless microphones and sets guidelines for frequency usage. It is important to follow these guidelines to avoid interference with other devices and ensure optimal performance.
Frequently Asked Questions
What can cause radio interference?
Radio interference can be caused by a variety of factors, including other electronic devices, power lines, and even natural sources like lightning. In the case of wireless microphones, interference can be caused by other wireless devices operating on the same frequency band.
915 MHz interference: What is it and how to prevent it?
915 MHz interference is a type of interference that can occur when wireless microphones operate on the same frequency band as other devices that use 915 MHz, such as cordless phones and baby monitors. To prevent this type of interference, it is important to choose wireless microphones that operate on a different frequency band.
900 MHz interference: How to avoid it?
900 MHz interference is another type of interference that can occur when wireless microphones operate on the same frequency band as other devices that use 900 MHz, such as cordless phones and wireless speakers. To avoid this type of interference, it is important to choose wireless microphones that operate on a different frequency band.
GSM buzz: How to deal with it?
GSM buzz is a type of interference that can occur when a cell phone is placed near a wireless microphone. To deal with this type of interference, it is recommended to turn off or put the cell phone on airplane mode, or to keep the cell phone at a distance from the wireless microphone.
What causes interference with wireless microphones?
Interference with wireless microphones can be caused by a variety of factors, including other wireless devices operating on the same frequency band, physical obstructions, and even weather conditions. It is important to choose wireless microphones that operate on a different frequency band to prevent interference.
Does 5G interfere with wireless mics?
5G can potentially interfere with wireless microphones that operate on the same frequency band as 5G, which is in the 24-86 GHz range. However, most wireless microphones operate on different frequency bands, so interference with 5G is not a major concern for most users.
